A consortium of DIFFER, PSNC and Ignition Computing participating in the development of the ITER integrated modelling simulation framework, supported by the Netherlands eScienceCenter. This contract award is a validation of our integrated modelling and software development experience in the Netherlands and Poland.
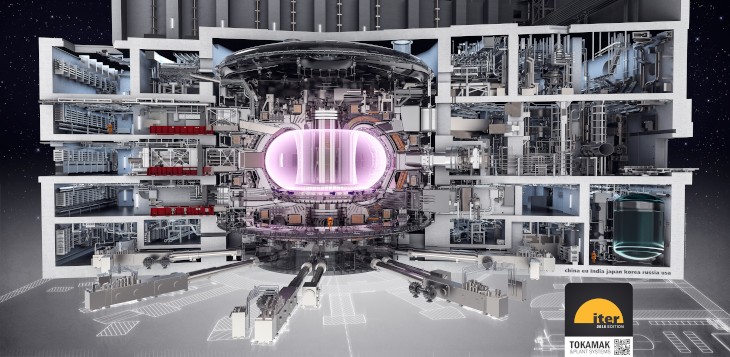
The international organisation ITER is building the largest tokamak in the world in France. This ‘big science’ project aims to prove useful power generation with nuclear fusion. This multi-billion USD project, built by partners in 35 nations, is one of the most complex machines ever built. Predictive modelling of this massive machine requires the coupling of many simulation tools and is a major task.
Most integrated modelling workflow tools use a directed acyclic graph (DAG) to organise operations. For co-simulation purposes, with an unknown number of iterations and many timestep loops, this paradigm is problematic. It is then better to work with semi-autonomous agents which exchange messages with each other, such as implemented in MUSCLE3, the Multiscale Coupling Library and Environment.
The Dutch Institute for Fundamental Energy Research (DIFFER) formed a consortium together with Ignition Computing and Poznan Supercomputing and Networking Center (PSNC), advised by the Netherlands eScienceCenter (NLeSC), which co-developed MUSCLE3, to submit the winning bid on an ITER call for the development of a persistent actor simulation framework.
In the coming year we will build a framework for ITER, based on MUSCLE3. This will be an integral part of the ITER integrated modelling strategy, which is essential for optimal operation of the reactor.
The opinions expressed in this article are those of Ignition Computing only and do not represent the ITER Organization’s official position.